2022. 8. 25. 08:08ㆍ✨ Linux
Intro
여느때처럼 disk partitioning 을 하는데 5번째 파티션을 만드는 순간 다음과 같은 에러가 발생했다.
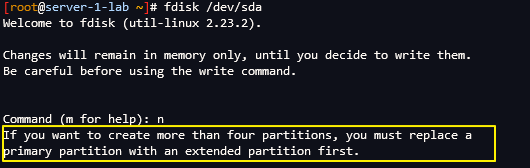
If you want to create more than four partitions, you must replace a
primary partition with an extended partition first.primary partiton 을 extended partition 으로 변경해야 한다고 한다.
결론부터 말하자면 MBR (MS-DOS) 타입의 Partition table을 사용하는 디스크는 Primary 파티션을 최대 4개까지 생성 가능하다.
파티션을 5개 이상 생성하려면 extended partition 을 하나 생성하고 나머지를 logical partition 으로 만들어야 한다.
왜 이런지 좀 찾아봤는데 다음 주제들에 대해 한번 정리 해보고자 한다.
- Disk Partitioning table : MBR과 GPT의 차이
- MBR - Primary / Extended 파티션의 이해
- MBR - Extended 파티션 사용하여 5개 이상의 파티셔닝 하기
Disk Partition table : MBR과 GPT의 차이
Partition Table이란?
Partition Table은 하드 디스크의 파티셔닝 정보를 OS 에 제공하는 역할을 한다.
파티션 테이블의 주요 타입으로는 MBR과 GPT가 있다.
MBR (Master Boot Record, MS-DOS)
MBR 타입에서는 파티셔닝 정보를 드라이브의 시작 지점에 위치한 Boot sector(MBR)에 저장한다.
파티션 수, 파티션 별 파일 시스템 유형, 부팅 가능 여부 등이 저장된다.
여기서 Boot Sector에 대해 자세하게 설명하지는 않으며, 나는 다음 게시글을 읽어보기만 했다.
https://knowitlikepro.com/understanding-master-boot-record-mbr/
MBR 타입은 다음과 같은 두 단점이 있다.
-- Parimary 파티션을 최대 4개까지만 생성할 수 있음
-- Disk 파티션은 2TB를 넘지 못함
GPT 타입을 사용하면 MBR의 이러한 제약사항을 보완할 수 있다.
GPT (GUID Partition Table)
GPT은 MBR 타입 보다 장점이 많은 새로운 파티션 테이블 타입이다.
MBR 타입과 달리 디스크 파티셔닝 및 OS 부팅에 관련된 코드를 GPT 헤더에 담아 디스크 전체에 전반적으로 저장한다.
그래서 하나의 파티션이 손상되어도 부팅 및 일부 데이터 복구가 가능하다고 한다.
MBR은 최대 4개의 primary 파티션 생성이 가능한 것에 반해, GPT 타입은 최대 128개까지 만들 수 있다.
MBR과 GPT 파티션 테이블 구조를 살펴보면 다음과 같다.
MBR 구조의 경우 Master Boot Record 영역이 테이블 시작 지점에 위치한다.
Primary Partition 3개 + Extendted 1개로 구성하여 Extended 파티션 안에서 여러개의 Logical Parition 을 생성한 것을 볼 수 있다.

MBR - Primary / Extended 파티션의 이해
이제 앞서 파티셔닝 하려던 /dev/sda 디바이스가 MBR 타입이라서 다섯번째 primary 파티션 생성이 불가능했던 것의 연관 관계를 알게 되었다.
그렇다면 Primary / Extended Partition 은 무엇일까?
Primary Partition?
Primary 파티션은 OS 부팅 가능한 파티션이다.
즉, OS 를 설치할 수 있는 공간이다.
(각 primary partition 에 서로 다른 OS를 설치하고 grub 상에서 어떤 primary 파티션으로 부팅할건지 선택하여 multi-os 로 운영할 수도 있다고도 한다.)
Extended Partition?
Extended 파티션은 부팅 불가능하고 데이터 저장용으로 쓰이는 파티션이다.
MBR 타입에서는 마지막 4번째 파티션을 Extended로 구성하고, 그 안에 여러 logical 파티션을 생성하여 사용할 수 있다.
logical 파티션 또한 부팅 불가능하고 데이터 저장용도로만 쓰인다. Extended 파티션에 여유 공간이 있으면 logical 파티션은 개수 상관 없이 만들 수 있다.
MBR - Extended 파티션 사용하여 5개 이상의 파티셔닝 하기
Primary 로 생성했던 /dev/sda4를 삭제한 다음 extended 타입으로 지정해서 만든다.
[root@server-1-lab ~]# fdisk /dev/sda -l
Disk /dev/sda: 2147 MB, 2147483648 bytes, 4194304 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 4194304 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x000d0a4b
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 8192 204799 98304 8e Linux LVM
/dev/sda2 204800 466943 131072 83 Linux
/dev/sda3 466944 671743 102400 83 Linux
/dev/sda4 671744 876543 102400 83 Linux
[root@server-1-lab ~]# fdisk /dev/sda
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2).
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command.
Command (m for help): d
Partition number (1-4, default 4):
Partition 4 is deleted
Command (m for help): n
Partition type:
p primary (3 primary, 0 extended, 1 free)
e extended
Select (default e): e
Selected partition 4
First sector (671744-4194303, default 671744):
Using default value 671744
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (671744-4194303, default 4194303):
Using default value 4194303
Partition 4 of type Extended and of size 1.7 GiB is set
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
WARNING: Re-reading the partition table failed with error 16: Device or resource busy.
The kernel still uses the old table. The new table will be used at
the next reboot or after you run partprobe(8) or kpartx(8)
Syncing disks.이제 /dev/sda4가 Extended Partition 이 되었다.
[root@server-1-lab ~]# fdisk /dev/sda -l
Disk /dev/sda: 2147 MB, 2147483648 bytes, 4194304 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 4194304 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x000d0a4b
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 8192 204799 98304 8e Linux LVM
/dev/sda2 204800 466943 131072 83 Linux
/dev/sda3 466944 671743 102400 83 Linux
/dev/sda4 671744 4194303 1761280 5 Extended5개 이상의 파티션을 생성해 본다.
[root@server-1-lab ~]# fdisk /dev/sda
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2).
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command.
Command (m for help): n
All primary partitions are in use
Adding logical partition 5
First sector (679936-4194303, default 679936):
Using default value 679936
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (679936-4194303, default 4194303): +256M
Partition 5 of type Linux and of size 256 MiB is set
Command (m for help): n
All primary partitions are in use
Adding logical partition 6
First sector (1212416-4194303, default 1212416):
Using default value 1212416
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (1212416-4194303, default 4194303): +200M
Partition 6 of type Linux and of size 200 MiB is set
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered!logical partion 으로 /dev/sda5, /dev/sda6 이 생성 되었다.
[root@server-1-lab ~]# lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sda 8:0 0 2G 0 disk
|-sda1 8:1 0 96M 0 part
| `-examvg-exam_lv 253:0 0 92M 0 lvm /data
|-sda2 8:2 0 128M 0 part
|-sda3 8:3 0 100M 0 part
|-sda4 8:4 0 1K 0 part
|-sda5 8:5 0 256M 0 part
`-sda6 8:6 0 200M 0 part
vda 252:0 0 30G 0 disk
`-vda1 252:1 0 30G 0 part /참고 문서
- https://www.differencebetween.com/difference-between-primary-partition-and-vs-extended-partition/#:~:text=Primary%20partition%20is%20a%20bootable,is%20used%20to%20store%20data.
- https://www.baeldung.com/linux/partitioning-disks#:~:text=MBR%20(Master%20Boot%20Record)%20and,four%20primary%20partitions%20are%20allowed
- https://www.howtouselinux.com/post/mbr-vs-gpt
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/computer-science/partition-table
'✨ Linux' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 로컬 yum 레포지터리 만들기! (reposync, yumdownloader, createrepo) (0) | 2022.08.28 |
|---|---|
| lvm 구축한 것 삭제하기 (lvremove, vgremove, pvremove) (0) | 2022.08.27 |
| SNAT / DNAT 개념과 iptables 에 NAT 룰 적용해보기 (0) | 2022.08.13 |
| Shell Script 짜면서 찾아봤던 것들 (0) | 2022.08.11 |
| dd 명령어 개념과 손쉽게 더미 파일 생성하기 (0) | 2022.08.09 |
